Fighting Fibromyalgia
Diagnosing And Treating The Chronic Pain Disorder
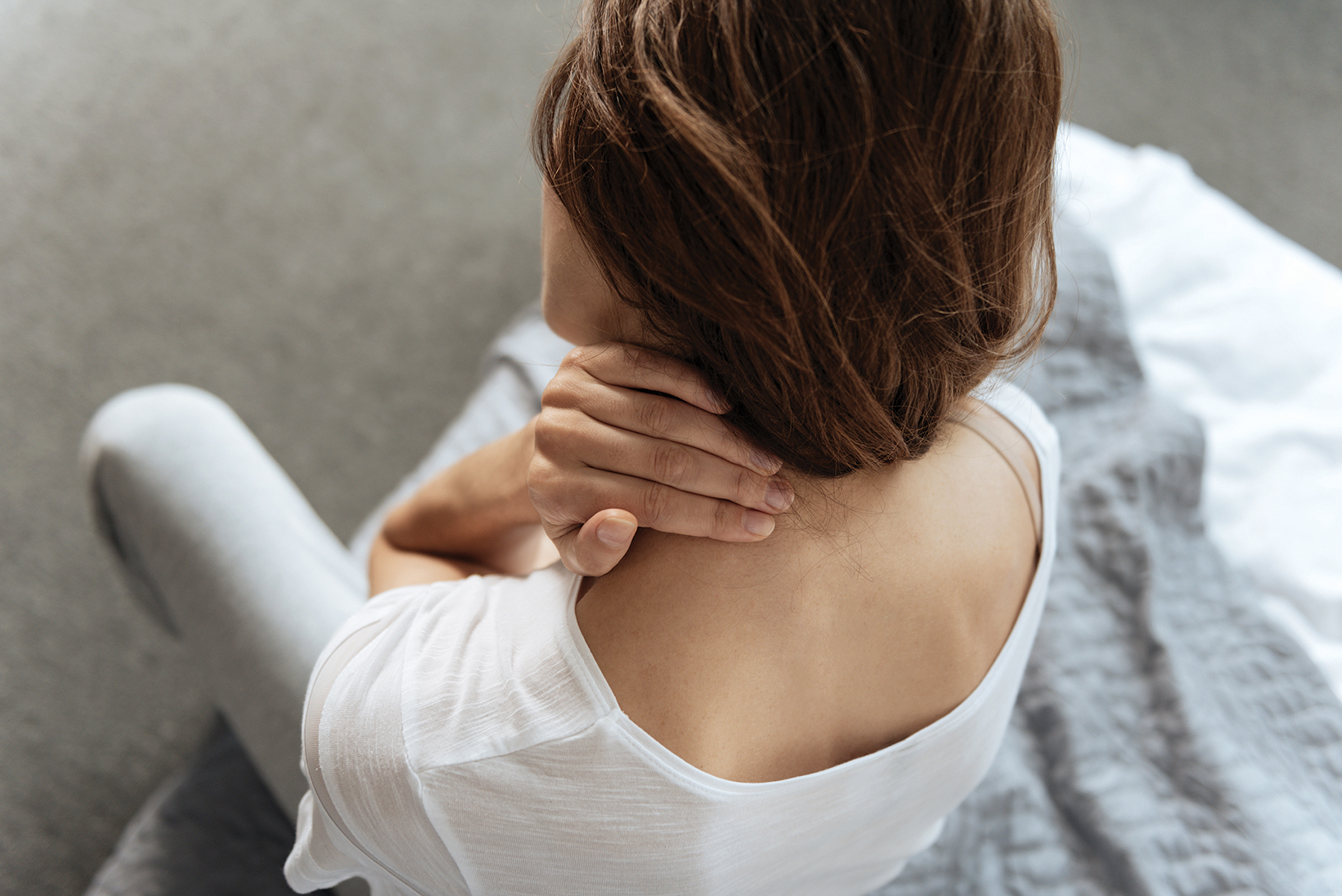

Diagnosing fibromyalgia can be difficult because many of the symptoms can be the onset of something else. Fibromyalgia can cause chronic pain and fatigue similar to arthritis. When this happens, your primary care physician may ad-vise you to see a rheumatologist to rule out other conditions. As a result, often a rheumatologist diagnoses fibromyalgia.
Dr. Mary Anne Dooley, a board-certified rheumatologist at WakeMed Physician Practices – Rheumatology in North Raleigh, shares some insight on fibromyalgia.
What is Fibromyalgia?
Fibromyalgia is a chronic pain disorder characterized by widespread muscle pain throughout the body. It is important to note that fibromyalgia is not an autoimmune disease or a form of arthritis. Although it is impossible to diagnose by a lab test or X-ray, fibromyalgia can be accompanied by sleep disturbances, muscle tenderness, fatigue, and mood issues. Fibromyalgia affects roughly two to four percent of people, mostly women.
Fibromyalgia Symptoms
Many symptoms of fibromyalgia overlap with early rheumatoid arthritis and lupus, which is why it can be hard to diagnose. Symptoms include: pain; sleep disorders (more common in women); Irritable Bowel Syndrome; chronic headaches; depression; fatigue; and hypersensitivity.
Diagnosing Fibromyalgia
While there is no test to detect fibromyalgia, you may need lab tests or x-rays to rule out other health problems. For those with the condition, musculoskeletal pain is the most common symptom. Pain and tenderness is typically centralized around the joints – not the joint themselves – and can be in: lower neck in front; edge of upper breast; below side bone at elbow; just above knee on inside; base of the skull; neck and shoulder; upper inner shoulder; upper outer buttock; and hip bone.
Treatment Options
There is no cure for fibromyalgia. However, symptoms can be treated with medication as well as non-drug-based treatments. Conditioning exercises (walking, yoga, water aerobics, etc.), massage therapy, physical therapy, and even simple lifestyle changes like a healthy diet and vitamin supplements are often very effective approaches to managing symptoms. Speak to your rheumatologist about which treatment option is best for you.
The Role of the Rheumatologist
Discuss your symptoms with a rheumatologist to ensure there are no other causes for your symptoms. If fibromyalgia is diagnosed, he or she can discuss with you the current understanding of the syndrome, symptoms, and current treatment recommendations.
Fibromyalgia Resources
Dr. Dooley recommends the following resources for additional information and support:
– National Fibromyalgia & Chronic Pain Association (NfmCPA) Raleigh Support Group;
– American College of Rheumatology;
– University of Michigan Chronic Pain and Fatigue Research Center.
WakeMed Physician Practices - Rheumatology
Rheumatic conditions can be difficult to diagnose, manage, and treat – and can have a significant impact on patients’ quality of life. That’s why WakeMed Physician Practices – Rheumatology is committed to providing patients with a personalized approach to care to help you manage your complex rheumatic disease. Dr. Mary Anne Dooley makes personalized treatment recommendations to help people experiencing joint pain, musculoskeletal pain, fatigue, or other symptoms related to autoimmune disorders.
- 919-235-6454